The need for maintenance
Explains why inspections are needed when using gas detectors, along with the legal background and the risks of failing to perform inspections.
Explains why inspections are needed when using gas detectors, along with the legal background and the risks of failing to perform inspections.
Gas monitors are designed to ensure safety and peace of mind for all personnel working on a site.
This is why it’s extremely important to inspect and maintain products at regular intervals to ensure performance and to improve disaster-prevention and safety reliability during use. Maintenance consists of the following three types of tasks:
Maintenance types
・Daily maintenance consists of visual inspections carried out by workers before work.
・Monthly maintenance consists of inspections (alarm tests) of alarm circuits carried out by workers once a month.
・Regular maintenance consists of inspections, including span adjustments, carried out once every six months by Riken Keiki service engineers to ensure safety performance.
Particularly in the case of special high-pressure gases, such maintenance and inspections are mandated by the Exemplified standards relating Exemplified standards relating to the Regulation on Safety of General High Pressure Gas (in Japan) as follows;
“Gas leak detection alarm systems for special high-pressure gas must be calibrated at least once every six months.”
Proper equipment maintenance helps maintain satisfactory equipment performance and function for extended periods and ensures safety against gas-related disasters.
The sensitivity of gas detectors may gradually degrade due to the following factors:
Causes of gas sensor deterioration
・Contact with substances that damage sensors
・Changes in the properties of the sensor component materials over long-term use
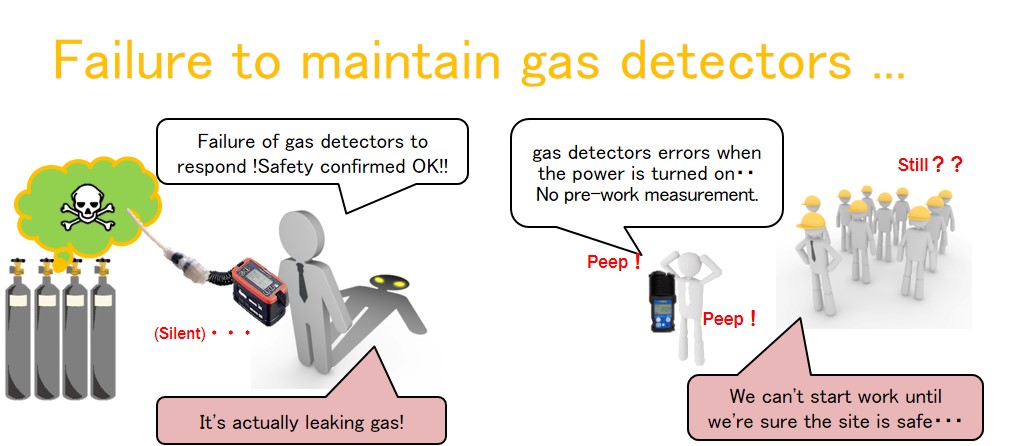
Inadequate maintenance may lead to gas accidents or work stoppages!
Failure to maintain gas detectors may result in the failure of gas detectors to respond when gas leaks occur or errors when the power is turned on, preventing work from being carried out safely.
Maintenance is divided into maintenance carried out by workers and maintenance carried out by specialist staff—for example, the manufacturer’s personnel.
Both types of maintenance must be performed at regular intervals to ensure high safety levels.
Maintenance types
User maintenance
Daily maintenance: Visual inspections carried out by workers before work.
Monthly maintenance: Inspections (alarm tests) of alarm circuits carried out by workers once a month.
Manufacturer maintenance
Regular maintenance: Inspections, including sensitivity calibrations, carried out once every six months by service engineers to ensure safety performance.
Specialist maintenance
Gas detectors are safety devices deployed to safeguard personnel from gas hazards across a wide range of harsh conditions.
For this reason, they must be maintained to ensure reliability.
Maintenance requires specialist knowledge and experience. In order to maintain the performance of your gas detector, please use our maintenance service.
[Why specialist knowledge is required]
・Gas detectors vary greatly in configuration and operating methods depending on the type.
・Some detection target gases may be highly chemically active or occur in extremely low concentrations. They must be handled appropriately based on the characteristics of the gas.
・Caution is required during gas calibration and any other handling of hazardous substances.
Gas detectors must undergo maintenance and inspections at regular intervals to ensure performance and to maintain disaster prevention and safety reliability.
For more information on maintenance and inspection specifics, please refer to the corresponding product instruction manual.
Some typical maintenance details are described below.
| Maintenance item | Maintenance details | Daily maintenance |
Monthly maintenance |
Regular maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power supply check | Check to confirm that the power lamp is lit. | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Concentration display check | Confirm that the concentration readout is zero ([20.9] (vol %) for oxygen). If the reading is offset, confirm that no interference gas is present in the vicinity and perform zero calibration (air calibration). |
○ | ○ | ○ |
| Flow check | Check the flow display and confirm the absence of any abnormalities. | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Filter check | Check to confirm that the dust filters are not dirty or clogged. | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Alarm test | Use the alarm test function to check the alarm circuit. | ○ | ○ | |
| Calibration | Perform calibration using a calibration gas. | ○ | ||
| Gas alarm check | Check the gas alarm using a calibration gas. | ○ |
Daily maintenance: Perform maintenance before work.
Monthly maintenance: Inspect the alarm circuit (alarm test) once a month.
Regular maintenance: Perform maintenance at least once every six months to ensure safety performance.
Regulations governing the safety of high-pressure gases specify the following maintenance requirements for gas leak detection alarm systems that use fixed products:
Exemplified standards relating to the Regulation on Safety of General High Pressure Gas
23. Gas leak detection alarm systems and installation locations
1. Function
1.8
Detection and alarm systems must be periodically inspected and maintained in accordance with the inspection and maintenance items described in the operating manual or specifications. Inspection and maintenance records must be retained for at least three years.
1.9
Gas leak detection alarm systems for special high-pressure gas must be calibrated at least once every six months.
1.10
Detection alarm systems must undergo alarm tests involving the alarm circuit at least once a month. Detection and alarm functions must be tested at least once a year.
Calibration gas, tools, and the equipment we have used in processes up to the point at which a gas detector is shipped are traceable back to national standards.
We can issue a traceability certificate as a declaration of conformity to certify calibration using in-house standard devices traceable back to national standards.
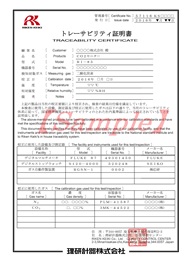
| Document title | Details | |
|---|---|---|
| a | Traceability certificate front page | Customer name, information on product covered by traceability certificate, calibration information |
| b | Gas inspection record sheet * If cylinder gas is used for calibration |
Inspection certificates issued by cylinder gas supplier (Generally one year if the cylinder validity period has not expired) |
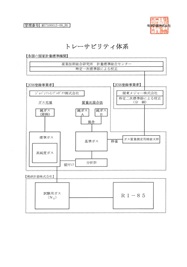
| c | Traceability system | Traceability system diagram for the gas manufacture |
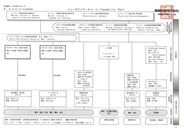
| d | Traceability chart | Traceability system diagram for equipment and measuring devices |
| a | b | c | d |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Riken Keiki operates a network of sales and maintenance offices in Japan and worldwide.
We ensure that our service engineers undergo regular maintenance training and certification to constantly improve our high-quality maintenance services.